- By Marissa Morales-Rodriguez, PhD, Penny Chen, PhD, Peter Fuhr, PhD, Sterling Rooke, PhD
- InTech
Summary
Fast Forward
- IIoT may essentially become IoT with components wrapped in a harder shell.
- IIoT benefits from data flowing through standards-based and common networks. From a networking standpoint, the IIoT systems will break the practice of using proprietary networks and put into place a common standards-based networking technology.
- The convergence of the IT and OT knowledge for industrial automation environments is well underway. Soon IIoT will approach the network edge for almost every industrial application.

Industrial Internet of Things evolution
By Peter Fuhr, PhD; Marissa Morales-Rodriguez, PhD;
Sterling Rooke, PhD; and Penny Chen, PhD

Experienced owner-operators of industrial facilities recognize the buzz surrounding the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), but often shun the notion of consumer-grade devices being installed and integrated into an operational control system. During the ISA Process Control and Safety Forum (PCS) in Houston, Texas, in November 2016, ISA's Communication Division convened a panel to focus on IIoT. Experienced industrial and control engineers on the panel expressed concerns and reservations with IIoT. Whereas some acknowledged an interest in the topic, others did not recognize it as an inevitable part of the industrial controls landscape. Granted, IIoT is still mostly a vision in the instrumentation and automation landscape; however, its place on stage is coming into view. During the opening session of PCS 2016, ISA President Jim Keaveney rhetorically asked the audience if IoT had peaked and also wondered if "cyber" would be the next area for innovation. This article explores the nexus of "domestic" IoT and how product evolution will drive its development toward that of IIoT.
U.S. government to promote IIoT evolution?
On 1 September 2016, the National Telecommunications and Information Administration within the U.S. Department of Commerce (DOC) conducted an IoT workshop. Discussions included how IoT and IIoT were set to converge around common threads. An important area of convergence will occur around onboard components and subsystems, with software as a runner-up because of cost and the innate drive to be first to market. However, as the recent Samsung Note 7 battery failure and subsequent recall has shown, releasing a product with flaws that are later discovered in the field by your customers is a bad idea. Despite this, the hype surrounding IoT is truly at its peak relative to other emerging technologies.
President Trump has targeted infrastructure as a key agenda item in his administration. This proposed infrastructure buildout combined with growth in U.S. industrial capacity would benefit from incorporation of IIoT sensors and systems. At the Consumer Electronics Show (CES) in January 2017 in Las Vegas, many companies demonstrated attempts to deploy IIoT in industrial facilities-often with woefully inadequate performance and cybersecurity. The rush to develop and deploy will no doubt increase consumer IoT being used for IIoT (again, as on display at CES 2017), accelerating the IoT and IIoT convergence.
At the DOC IoT workshop, participants spent a significant amount of time discussing the important role government can play in setting IoT standards. IoT experts at the workshop made it clear that with assistance from the federal government-specifically the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and DOC and their national laboratories-guidelines for cybersecure and robust IoT could be developed. With help from the government and organizations such as ISA, industry will have a clearer path to develop industry-centric IIoT rather than rushing to field consumer IoT devices. The question is that, even with this framework, will simple cost and a discount of risk dominate, so that IIoT essentially becomes IoT wrapped in a harder shell? We propose that this is what will occur.
However, we must take heed when it comes to cybersecurity and realize that with commercial IoT, an industrial target could be attacked in a manner similar to an attack on a commercial target-but with very different consequences. The solution? Although we should accept that IoT and IIoT will converge, there must be clear distinctions in cyberarchitecture and associated protections. This goes for implementation as well as regulations and guidelines proposed by governments and industry standards developed by organizations like ISA.
Industrial Internet of Things
Could seemingly trivial items, such as Amazon Echo/Alexa, be worthy of consideration for industrial automation and applications? Many stalwarts of the status quo voice concerns about safety standards and dangers of this technology in the industrial setting. Although these are valid concerns, a more important concern is that commercial IoT standards or best practices do not always apply to IIoT concerns.
IIoT is a specialized IoT implemented in ruggedized packages suitable for industrial application environments. In fact, legacy industrial control devices, such as programmable logic controllers, will be compatible-for the time being-with IIoT running alongside. IIoT benefits from data flowing through standards-based and common networks. From a networking standpoint, the IIoT systems will break the ongoing practice of using proprietary networks and bring into place a common standards-based networking technology. The convergence of IT and operational technology (OT) operation knowledge for industrial automation environments is well underway. Soon IIoT will approach the network edge for almost every industrial application. IIoT installations can include hundreds or even thousands of sensors across a large facility. To handle all of this information, one approach is for IIoT to leverage the cloud in a manner similar to the Alexa example with IoT. In his book Internet of Things with Python, Gaston Hillar illustrates how sensor readings from IoT devices compound into a situation that must be managed.
A typical industrial practice involves acquiring one measurement per second from each IoT device. The number of measurements-from just one device-is:
- 60 measurements for all the variables per minute
- 3,600 (60 x 60) measurements per hour
- 86,400 (3,600 x 24) measurements per day
- 31,536,000 (86,400 x 365) measurements per year (assuming a nonleap year)
Consider the situation where an industrial facility has 3,000 IIoT devices running the same code, thereby generating 94,608,000,000 (31,356,300 x 3,000) measurements per year. (Each IIoT device is generating one reading per second.) In addition, it is envisioned that a data ingestion engine may analyze and acquire information from other data sources, such as tweets about weather-related issues in the locations in which the sensors are capturing data. The net result is huge volumes of both structured and unstructured data to analyze computationally to reveal patterns and associations.
From a convergence standpoint, many of these big data repositories and data manipulation centers will be the same for both IoT and IIoT. The key differences are cost and technical capability, and these commercial repositories are quite capable of servicing IIoT data at a low cost. Comingling of data between a home toaster oven (IoT) and the IIoT data from a cement kiln, for example, is not the real worry. The greater concern is a denial of service attack on the large provider. If we consider Amazon and its Amazon Web Services (AWS) and similar technologies, we can appreciate how an attack on a commercial business such as Amazon could disrupt critical processes supported by IIoT in a factory.
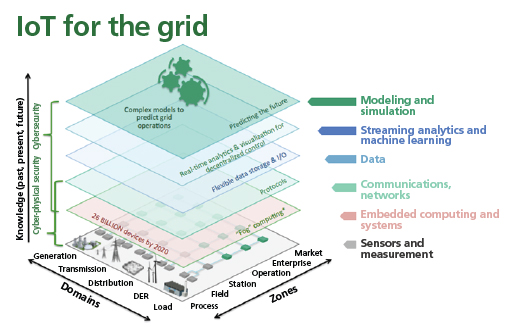
What constitutes IoT and the technology levels associated with IoT use in, for example, the electric grid? Figure 1 illustrates the situation.
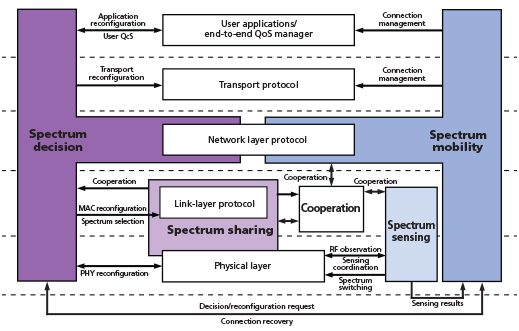
Figure 2. Spectrum sensing, sharing, decision, and mobility functional components of an IoT device for dense deployments in industrial settings
Intersecting technologies
With the introduction and promulgation of IoT devices in an industrial setting, a wide range of questions and problems arise, including the following examples:
1. How do wireless IoT devices all share the frequency spectrum? Issues of spectrum congestion-such as numerous devices sharing the same frequency spectrum-are lumped into the general category of the "spectrum crunch." One example of the correct answer can be for the IoT device to incorporate levels of spectrum sensing (in essence acting as a spectrum analyzer for the frequencies of "interest"), while having spectrum mobility (being able to change operating frequencies easily and quickly). The spectrum subsystem elements for such an adaptable IoT device are shown in figure 2.
2. Process control systems speak a wide range of protocols. Should an IIoT device or system speak one or all of these protocols? Or is having a logical system element perform protocol translation sufficient?
3. "IP addressable to the edge," such as most IoT device and system designs, causes the logical element and subsystem design-which is foundational to the vast majority of today's industrial networks-to be incorrect. IP-to-the-edge can provide wonderful integration into IT-centric networks, thereby allowing IT security applications to have entire network visibility. A "flat architecture" provided by IP-to-the-edge allows for an everything-to-everything level of connectivity. It also allows users to partition a variety of working zones based on operational or business needs. We believe the constraints should be set by application and business needs, not by technology incompatibility. This should be one basic concept of IIoT.
4. IoT movement has also advanced sensing technology. IoT edge devices may have varying levels of complexity and functionality, with various vendors leaning toward sophisticated and relatively energy-consumption-intensive operation, whereas others promote the advancing technology of passive wireless sensor tags (with no batteries, extremely low cost, and intrinsically safe operation). The ISA Communications Division has collaborated with the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration, DOE, and other organizations during the past six years to conduct passive wireless sensor tag workshops and promote new types of low-cost wireless sensing technologies for IIoT.
5. In essence, the question distills to the following: What does the industrial network have to look like for IIoT devices to be used? Several great standardization activities have been initiated in IEEE and the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), such as IEEE 802.1 Time Sensitive Networking and the IETF Deterministic Networking. Those technologies are created to address the need of IIoT, which allows a single network to share its resources and to be deterministic to reserve network bandwidth for time-critical applications. An initial set of functionality and performance "answers" for IoT devices in a factory automation setting is provided in figure 3.
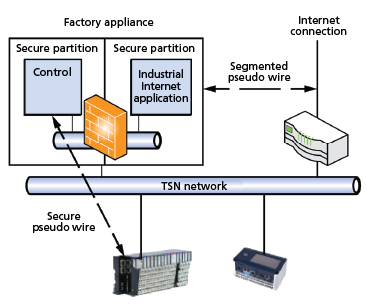
1. Communicate outside the plant in standard
ways
2. Have object-oriented data models that
relate to their physical objects
3. Not interfere with the reliability, integrity,
or security of control applications
4. Be portable to devices on the plant floor
5. Share the existing infrastructure
6. Anticipate various forms of wireless media
7. Be able to easily add or reconfigure applications
without affecting the existing plant.
Figure 3. An industrial Internet-ready, time-sensitive network architecture
Reader Feedback
We want to hear from you! Please send us your comments and questions about this topic to InTechmagazine@isa.org.
